Difference between revisions of "CAN Communication"
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
| − | + | ioThreadProc(void* inst) | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="cpp"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="cpp"> | ||
// CAN communication thread | // CAN communication thread | ||
| Line 86: | Line 86: | ||
case ID_RTR_FINGER_POSE_4: | case ID_RTR_FINGER_POSE_4: | ||
{ | { | ||
| − | |||
int findex = (id & 0x00000007); | int findex = (id & 0x00000007); | ||
| − | |||
vars.enc_actual[findex*4 + 0] = (short)(data[0] | (data[1] << 8)); | vars.enc_actual[findex*4 + 0] = (short)(data[0] | (data[1] << 8)); | ||
vars.enc_actual[findex*4 + 1] = (short)(data[2] | (data[3] << 8)); | vars.enc_actual[findex*4 + 1] = (short)(data[2] | (data[3] << 8)); | ||
vars.enc_actual[findex*4 + 2] = (short)(data[4] | (data[5] << 8)); | vars.enc_actual[findex*4 + 2] = (short)(data[4] | (data[5] << 8)); | ||
vars.enc_actual[findex*4 + 3] = (short)(data[6] | (data[7] << 8)); | vars.enc_actual[findex*4 + 3] = (short)(data[6] | (data[7] << 8)); | ||
| − | |||
// convert encoder count to joint angle | // convert encoder count to joint angle | ||
| Line 109: | Line 106: | ||
break; | break; | ||
} | } | ||
| − | |||
default: | default: | ||
| Line 118: | Line 114: | ||
return NULL; | return NULL; | ||
} | } | ||
| − | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
Revision as of 13:41, 2 July 2019
CAN Communication Tutorial
Please download CAN_tutorial.zip file and follow below steps. File:CAN tutorial.zip
CAN_tutorial.zip contains CMakeList.txt, README and grasp directory.
CAN_tutorial.zip contains CMakeList.txt, README and grasp directory.
This tutorial will show how to open & close CAN communication. Also, how to get position data and send pwm to operate Allegro Hand. You will follow step by step with adding sample codes. Source code assumes you have a peak-systems pcan to usb adapter so if you are not using PEAK CAN device, please check your own device CAN api and channel.
simple diagram
Below picture shows a structure of a sample program for this tutorial.
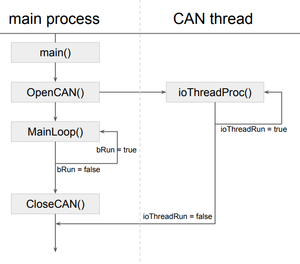
main.cpp
You can find main.cpp in grasp directory. There are 3 functions you have to edit.
OpenCAN() function initialize CAN I/O thread and start it.
// Open a CAN data channel bool OpenCAN() { printf(">CAN(%d): open\n", CAN_Ch); // CAN open int ret = command_can_open(CAN_Ch); if(ret < 0) { printf("ERROR command_can_open !!! \n"); return false; } // initialize CAN I/O thread ioThreadRun = true; pthread_create(&hThread, NULL, ioThreadProc, 0); printf(">CAN: starts listening CAN frames\n"); // set periodic communication parameters(period) printf(">CAN: Comm period set\n"); short comm_period[3] = {3, 0, 0}; // millisecond {position, imu, temperature} ret = command_set_period(CAN_Ch, comm_period); if(ret < 0) { printf("ERROR command_set_period !!! \n"); command_can_close(CAN_Ch); return false; } // servo on printf(">CAN: servo on\n"); ret = command_servo_on(CAN_Ch); if(ret < 0) { printf("ERROR command_servo_on !!! \n"); command_set_period(CAN_Ch, 0); command_can_close(CAN_Ch); return false; } return true; }
ioThreadProc(void* inst)
// CAN communication thread static void* ioThreadProc(void* inst) { int id; int len; unsigned char data[8]; unsigned char data_return = 0; int i; while (ioThreadRun) { /* wait for the event */ while (0 == get_message(CAN_Ch, &id, &len, data, FALSE)) { switch (id) { case ID_RTR_FINGER_POSE_1: case ID_RTR_FINGER_POSE_2: case ID_RTR_FINGER_POSE_3: case ID_RTR_FINGER_POSE_4: { int findex = (id & 0x00000007); vars.enc_actual[findex*4 + 0] = (short)(data[0] | (data[1] << 8)); vars.enc_actual[findex*4 + 1] = (short)(data[2] | (data[3] << 8)); vars.enc_actual[findex*4 + 2] = (short)(data[4] | (data[5] << 8)); vars.enc_actual[findex*4 + 3] = (short)(data[6] | (data[7] << 8)); // convert encoder count to joint angle for (i=0; i<MAX_DOF; i++) { q[i] = (double)(vars.enc_actual[i])*(333.3/65536.0)*DEG2RAD; } // print joint angles for (int i=0; i<4; i++) { printf(">CAN(%d): Joint[%d] Pos : %5.1f %5.1f %5.1f %5.1f\n" , CAN_Ch, i, q[i*4+0]*RAD2DEG, q[i*4+1]*RAD2DEG, q[i*4+2]*RAD2DEG, q[i*4+3]*RAD2DEG); } break; } default: printf(">CAN(%d): unknown command %d, len %d\n", CAN_Ch, id, len); } } } return NULL; }
CloseCAN()
// Close CAN data channel void CloseCAN() { printf(">CAN: stop periodic communication\n"); //close CAN listening thread if (ioThreadRun) { printf(">CAN: stoped listening CAN frames\n"); ioThreadRun = false; int status; pthread_join(hThread, (void **)&status); hThread = 0; } // CAN close printf(">CAN(%d): close\n", CAN_Ch); int ret = command_can_close(CAN_Ch); if(ret < 0) printf("ERROR command_can_close !!! \n"); }
| Whos here now: Members 0 Guests 0 Bots & Crawlers 1 |